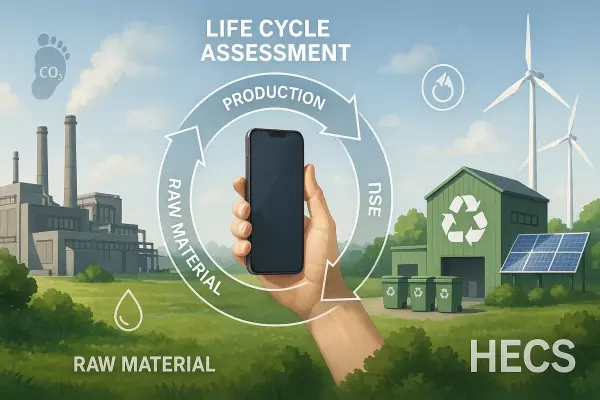

Climate change is no longer a distant threat—it's a present reality affecting businesses, governments, and individuals worldwide. As global carbon emissions continue to rise, innovative solutions are needed to combat this crisis. Enter carbon credits: a market-based mechanism that's revolutionising how we approach environmental responsibility.
But what are carbon credits exactly, and how do they work? Whether you're a business leader exploring ESG initiatives, a policymaker seeking compliance solutions, or simply an eco-conscious individual wanting to understand sustainability better, this guide will break down everything you need to know about carbon credits in simple, actionable terms.
What Are Carbon Credits?
Think of carbon credits like a currency for the environment. Just as you might trade dollars for goods, carbon credits allow you to trade environmental benefits.
In simple terms, a carbon credit represents the removal or reduction of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere. It's like having a certificate that says, "This action prevented one ton of greenhouse gases from entering our atmosphere."
Here's an easy analogy: imagine the atmosphere has a "pollution budget." When a company exceeds its budget by emitting too much CO₂, it can buy credits from someone who stayed under their budget or actively removed CO₂ from the air. It's environmental accounting that creates real-world impact.
The carbon credit system operates on a fundamental principle: one carbon credit equals one metric ton of CO₂ equivalent prevented or removed from the atmosphere.
Why Do Carbon Credits Exist?
Carbon credits didn't emerge in a vacuum—they're the result of global climate agreements and urgent environmental needs.
The Kyoto Protocol (1997) and later the Paris Agreement (2015) established international frameworks for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These agreements recognised that fighting climate change requires economic incentives, not just good intentions.
The goal is ambitious yet achievable: create market mechanisms that make reducing emissions profitable while penalising excessive pollution. By putting a price on carbon, these systems encourage businesses and nations to invest in cleaner technologies and sustainable practices.
Carbon credits transform environmental responsibility from a cost centre into a potential revenue stream, making sustainability economically attractive.
How Carbon Credits Work?
The carbon credit system operates through two main models: compliance markets and voluntary carbon markets.
Compliance Markets (Cap-and-Trade) Governments set emission limits (caps) for industries. Companies that emit less than their limit can sell excess credits to those exceeding their limits. This creates a trading system where reducing emissions becomes profitable.
Voluntary Carbon Markets Here, businesses and individuals voluntarily purchase credits to offset their carbon footprint. No government mandate exists—it's driven by corporate responsibility, ESG goals, or personal environmental commitment.
The process is straightforward: companies measure their emissions, set reduction targets, implement efficiency measures, and purchase credits to offset remaining emissions. This path leads toward carbon neutrality for business operations.
Carbon Offset Projects
Carbon credits originate from verified projects that either reduce emissions or remove CO₂ from the atmosphere. Popular carbon offset projects include:
Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees that absorb CO₂ as they grow
Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and hydroelectric projects replacing fossil fuels
Methane Capture: Capturing methane from landfills and agricultural operations
Clean Cookstoves: Providing efficient cooking solutions in developing countries
Energy Efficiency: Upgrading buildings and industrial processes
Direct Air Capture: Technology that pulls CO₂ directly from the atmosphere
These projects must be certified by recognised bodies like the Gold Standard, Verra (VCS), or the UNFCCC to ensure legitimacy and environmental impact. Certification guarantees that credits represent real, measurable, and additional emission reductions.
Benefits of Carbon Credits
Environmental Benefits: Carbon credits create tangible environmental improvements by funding projects that reduce global emissions. They accelerate the transition to renewable energy, protect forests, and support innovative clean technologies.
Economic Advantages For businesses, carbon credits offer multiple benefits:
Achieve net-zero emissions targets
Enhance ESG credentials and attract environmentally conscious investors
Meet regulatory compliance requirements
Generate new revenue streams from emission reduction projects
Build brand reputation as a sustainability leader
ESG carbon credits have become essential for companies seeking to demonstrate environmental responsibility to stakeholders, investors, and customers.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite their potential, carbon credits face legitimate challenges. The primary concern is greenwashing—using credits to appear environmentally responsible while avoiding meaningful emission reductions.
Other challenges include:
Ensuring project permanence (will that forest stay protected?)
Verifying additionality (would the project happen anyway?)
Measuring actual impact versus claimed benefits
Preventing double-counting of emission reductions
These issues highlight the importance of choosing high-quality, transparently verified credits from reputable certification bodies. Third-party validation and ongoing monitoring are essential for maintaining market integrity.
India's Role in Carbon Credit Markets
India is emerging as a significant player in global carbon trading. The country has launched various initiatives to develop domestic carbon markets and capitalise on its renewable energy potential.
Carbon trading India initiatives include the Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, which covers energy-intensive industries. Indian businesses increasingly recognise opportunities in carbon offset projects, from solar installations to waste management solutions.
With its vast renewable energy potential and growing focus on sustainability, India is well-positioned to become a major supplier of high-quality carbon credits while achieving its climate commitments.
The Path Forward
Understanding carbon credits is crucial in our collective fight against climate change. They're not a perfect solution, but they're a valuable tool in the broader sustainability toolkit.
The key is using carbon credits responsibly—as part of a comprehensive strategy that prioritises emission reductions first, then offsets remaining unavoidable emissions. When implemented correctly, carbon credits accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy while creating economic opportunities.
As businesses and individuals increasingly prioritise environmental responsibility, carbon credits will play an ever more important role in achieving global climate goals and building a sustainable future.
Looking to offset your carbon footprint or meet compliance targets?
Connect with HECS — your partner in environmental solutions, carbon assessments, and ESG compliance.
Share this post: